
 Dr. Abhishek Yadav
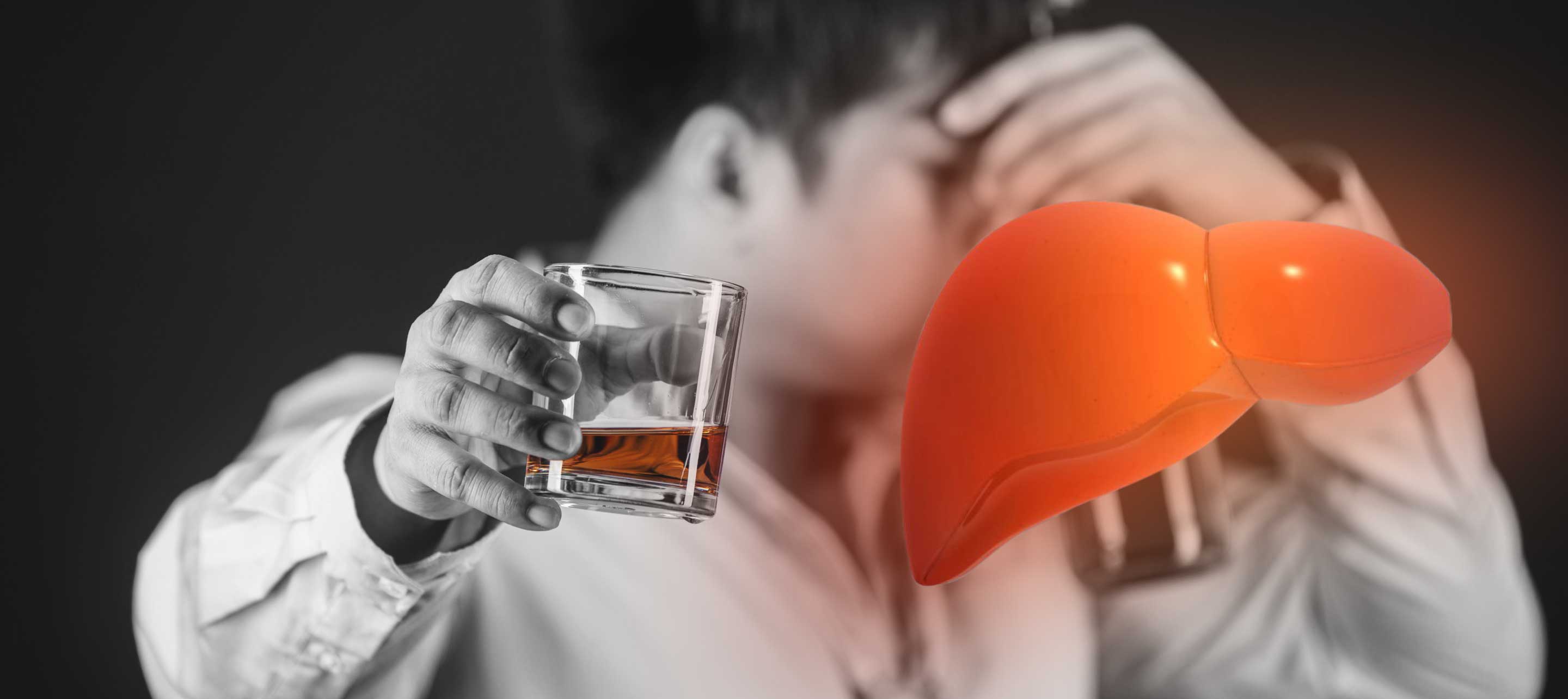
Dr. Abhishek YadavIn the entire world, alcohol is the drug that is most commonly abused. Excessive alcohol intake may manifest into alcoholic hepatitis which is amongst the most serious manifestations of alcohol-related liver disease. Alcoholic liver disease encompasses a range of complications, beginning from steatosis (fat build-up in liver tissue), developing into hepatitis (inflammation of liver tissue), and then manifesting into cirrhosis (liver tissue damage). Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption causes fatty changes in the liver that can progress from inflammation to cirrhosis.
Most chronic alcohol users do not eventually progress to severe liver disease. The observed variability in the outcomes implies that the susceptibility of individual patients to advanced liver disease may be influenced by a wide range of factors, including both hereditary and environmental.
Alcoholic hepatitis is an acute inflammation of the liver tissue that may affect patients who have steatosis or underlying cirrhosis. It is linked to significant disabilities and fatalities. The development of this disease is complex, involving not only genetic factors but also liver cell damage due to alcohol, free radicals, gut-derived microbial components, fat build-up, and activity of inflammatory cells (neutrophils and macrophages) in the liver.
Blood alcohol concentrations rise as a result of the gut's rapid absorption of alcohol during drinking. The liver cells metabolize most of the alcohol. Prolonged alcohol consumption combined with inflammatory agents activate fat storing cells, which leads to progressive liver tissue damage.
Schedule a call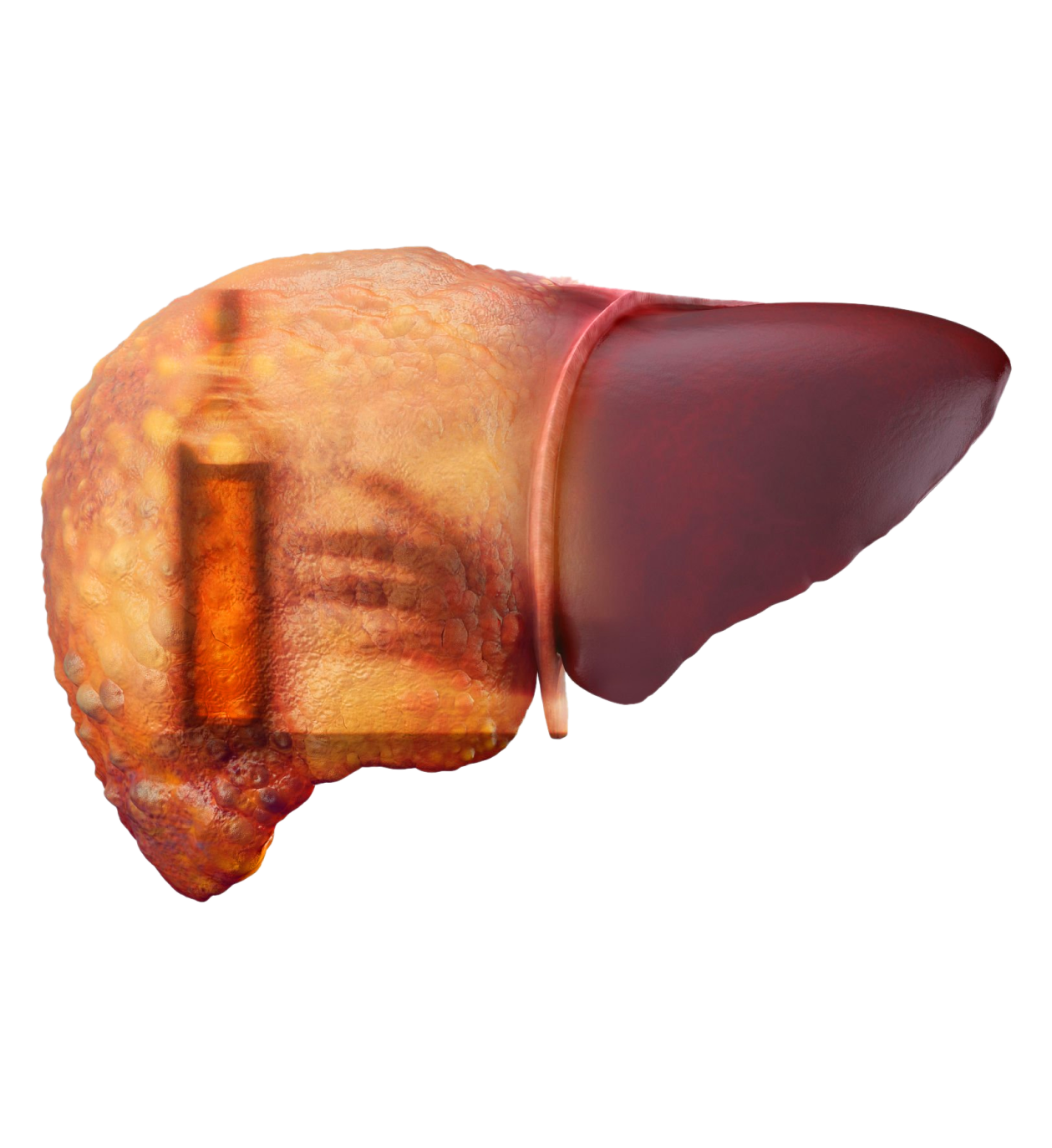
Get trustful insight about your liver problems and the accurate personalized treatment for it. Your well-being is important to us. Book your appointment for a second opinion.
Contact Us
 Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic HepatitisAlcoholic hepatitis is characterized by liver cell inflammation due to excessive and persistent alcohol abuse. It is an indication of tissue damage or infection caused by viruses, toxins, or excessive alcohol. The condition may only be a transient reaction to overindulgence. However, if alcohol-induced hepatitis progresses to a chronic state, your liver may sustain irreversible damage.
Your liver processes every food and beverage that you eat or drink. Your liver aids in the digestion of food and the removal of harmful substances. Alcohol becomes toxic when it is processed by your liver. It disintegrates it into toxic chemicals instead of providing any nutritional value.
Alcohol use disorder or heavy, chronic drinking can overload your liver with toxins and fat for processing. These toxins and fat accumulate and cause liver damage when your liver is unable to cope. There is an inflammatory reaction to the injury. This is your body's attempt to repair itself and prevent more damage.
Alcoholic hepatitis is primarily caused by heavy drinking over an extended period of time. Inflammation brought on by the liver's breakdown of alcohol has the potential to kill liver cells. The body gradually starts to replace healthy liver tissue with scars. This interferes with the liver's functions. Cirrhosis, or irreversible scarring, is the last stage of alcohol-related liver disease. Once cirrhosis develops, liver failure can occur rapidly. An injured liver may also obstruct the kidneys' ability to receive blood. Kidney damage and failure may follow from this.
Alcoholic hepatitis can be caused by other factors as well. For instance, the risk is higher in those with other forms of hepatitis. It is therefore not advised that they consume alcohol. Malnutrition is another complication of alcoholic hepatitis. Consuming large quantities of alcohol can cause appetite suppression. A person's primary source of calories may start to come from alcohol. Therefore, liver disease can also be exacerbated by malnutrition.
Following are the other risk factors:

With prolonged drinking, alcoholic hepatitis typically develops over time. However, severe alcohol-related hepatitis can strike without warning. Death and liver failure may even result from it. Alcoholic hepatitis can present following symptoms that may mimic other illnesses or issues:
Scarring of liver tissue is the cause of complications associated with alcohol-induced hepatitis. Hepatic blood flow can be slowed down by scar tissue. Toxin accumulation may result from this increase in pressure in the portal vein, a major blood vessel. Following are the associated complications:
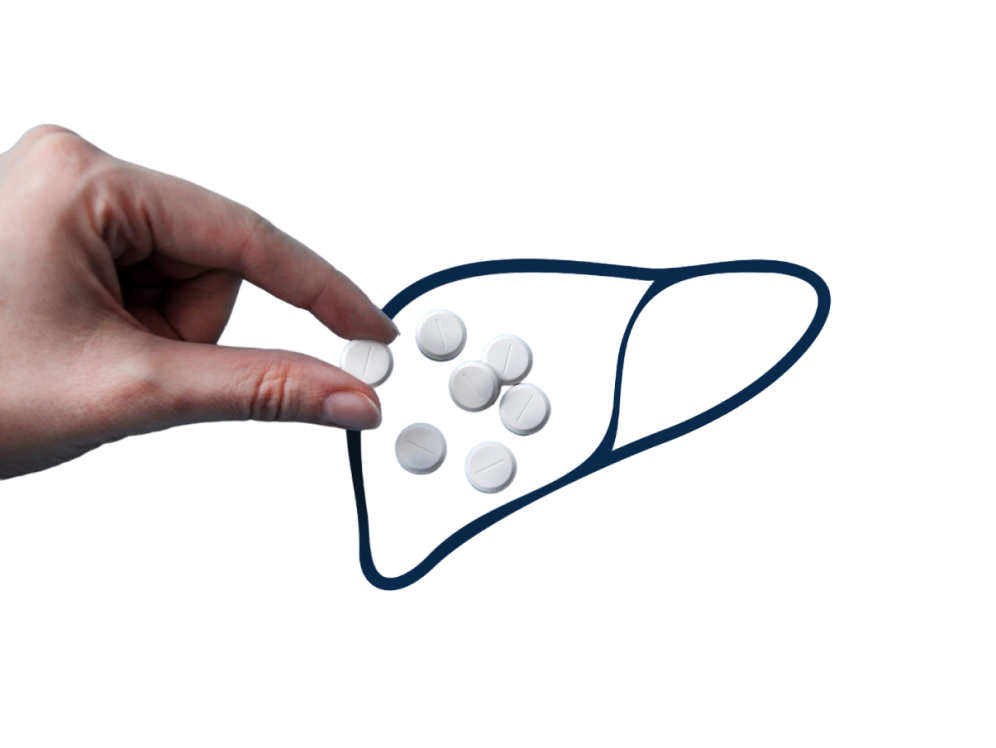

There is no specific medication for the treatment of alcohol-induced hepatitis. The only viable treatment option is alcohol cessation. It's advisable to stop it under proper medical supervision. There may be harmful side effects and withdrawal symptoms if you quit abruptly.
In addition to referring you for the treatment of alcohol use disorder, a liver specialist doctor can provide supportive care while you recover from alcohol withdrawal. They may also aid in the treatment of a few side effects brought on by alcohol consumption and hepatitis. Moreover, if hepatitis causes irreversible widespread severe scarring, then liver transplant can be considered.
Supplemental treatment modalities are:
Hepatitis caused by alcohol usually starts out silently and without any symptoms. Many people are unaware of the potential harm that heavy drinking on a regular basis may be doing to their livers. Your best chance of catching and curing alcohol-induced hepatitis, however, is early detection. Make an appointment with the Best Liver Specialist Doctor in Pune, India if you have a history of heavy alcohol use and/or liver disease symptoms. They will examine your liver, evaluate any potential harm, and assist you in altering your lifestyle for the better.
A: Liver scarring is irreversible. However, the liver can frequently reverse some of the effects of alcohol so that you can lead a normal life. You might receive outpatient care or be admitted to the hospital. Alcohol-related hepatitis cannot be cured with medication.
A: While complete alcohol cessation is often effective in treating mild to moderate forms of acute alcoholic hepatitis. But patients with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis have a poor prognosis.
A: If alcohol consumption persists, alcoholic hepatitis typically develops into cirrhosis. Hepatitis returns to normal in a few months for those who stop drinking, but the cirrhosis that has already set in does not go away.
A: The first phase is characterized by the buildup of fat within the liver cells, which is also referred to as fatty liver or steatosis. Alcohol use can occasionally result in alcoholic hepatitis if it continues past this point.
A: Alcohol consumption may result in hepatitis or liver edema and inflammation. This can eventually result in liver cirrhosis, the last stage of alcoholic liver disease. The cirrhosis results in irreversible damage.