 Dr. Abhishek Yadav
Dr. Abhishek YadavHepatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the liver tissue which manifests in several forms, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. It can have a wide range of causes. The distinction between acute and chronic hepatitis helps to manage the disease accordingly. If the body is unable to get rid of the virus after six months, it is diagnosed as chronic hepatitis.
Over 1.1 million people worldwide pass away each year from complications related to their hepatitis, including liver cancer and liver cirrhosis, and an estimated 354 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis B and C. A number of people who get infected with hepatitis remain unaware of it, which is why it is designated as the ‘silent killer'. Antiviral medications can treat chronic hepatitis B and cure the majority of hepatitis C cases, while safe and effective vaccinations can prevent hepatitis B. However, access to timely and accurate testing is necessary to achieve these hepatitis free outcomes and eradicate it as a threat to overall public health.
Schedule a call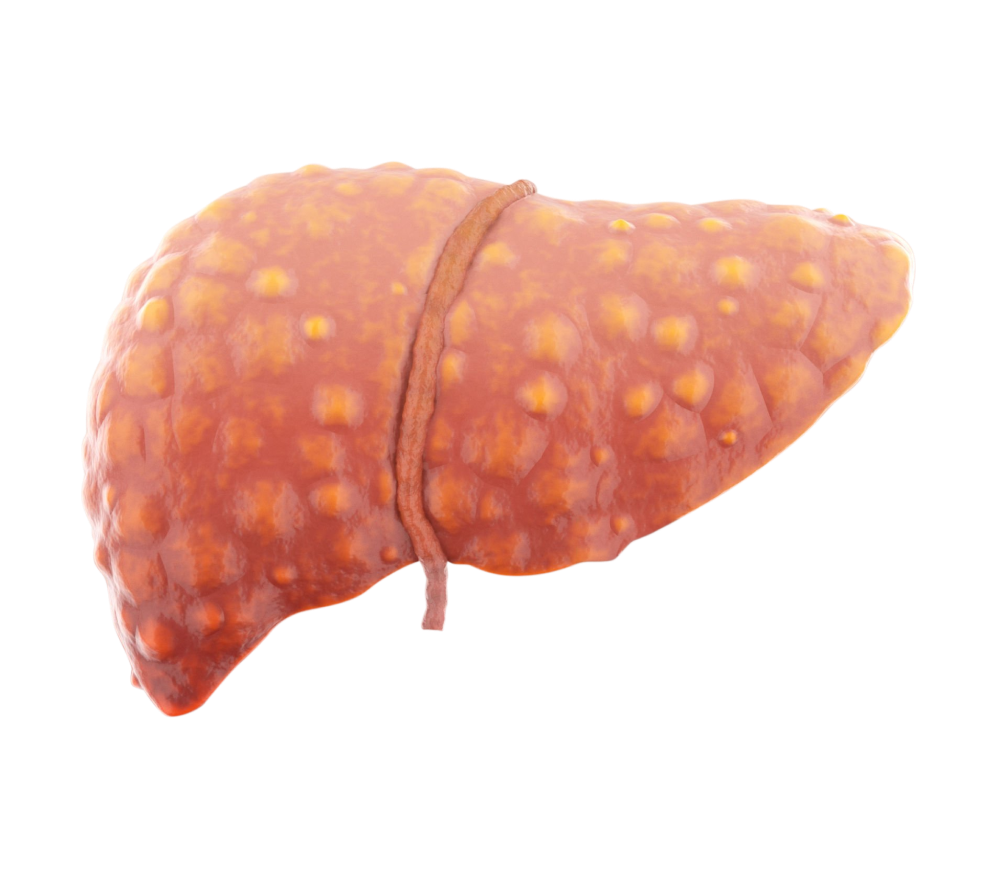
Get trustful insight about your liver problems and the accurate personalized treatment for it. Your well-being is important to us. Book your appointment for a second opinion.
Contact Us
 Chronic Hepatitis
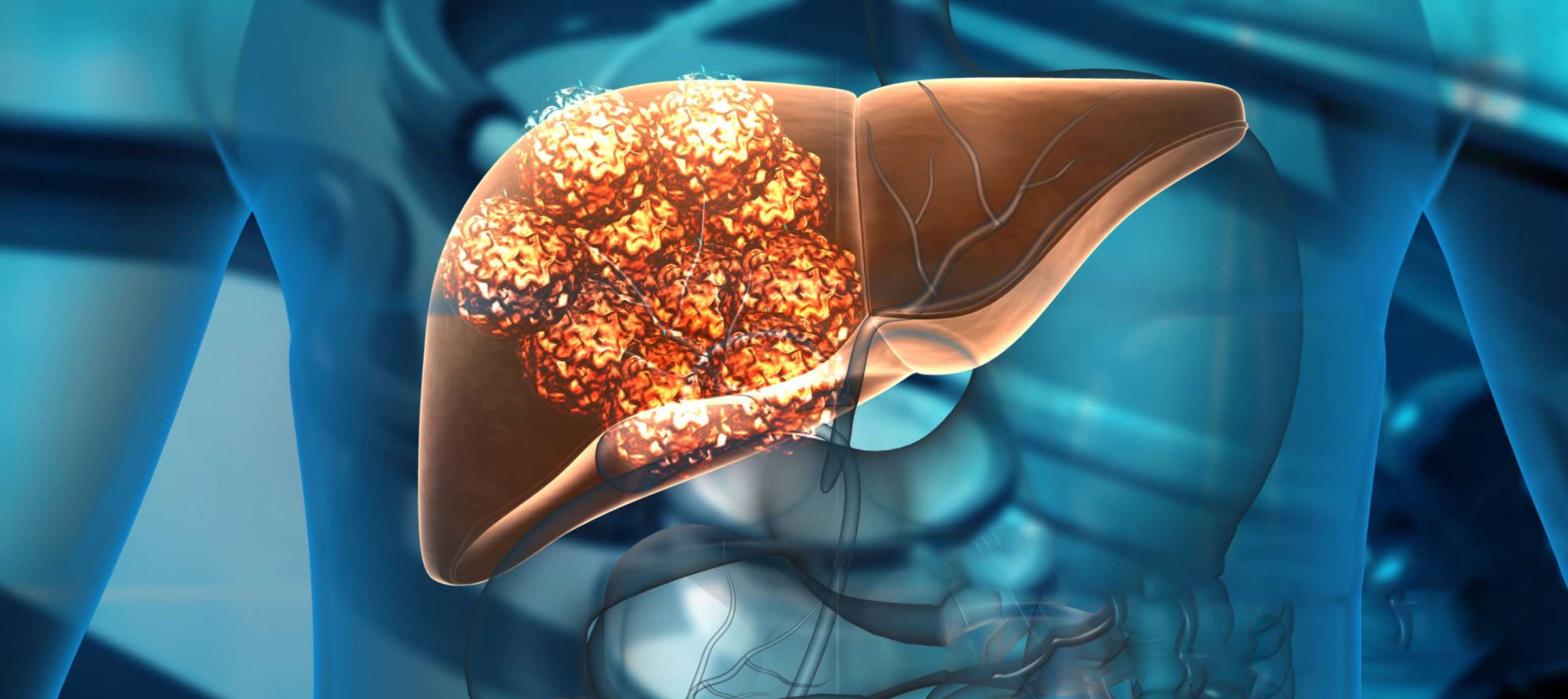
Chronic HepatitisThe inflammation of the liver tissue is known as hepatitis. Liver inflammation persists for more than six months in cases of chronic hepatitis. This disorder could be more serious and result in the destruction of many liver cells, or it could be mild and cause relatively little damage. Liver failure and cirrhosis may develop if the chronic hepatitis is not treated timely and appropriately.
 CONTACT US
CONTACT USChronic hepatitis happens due to both infectious and non-infectious causes:
Viral infections are the most common causes of chronic hepatitis. These are:
Chronic hepatitis may also happen due to non-infective causes:
May also cause chronic hepatitis, such as:
Chronic hepatitis is another side effect of certain drugs. However, prevalence of such hepatitis is rare. When patients are prescribed medications that are known to cause hepatitis, periodic blood tests are necessary. Early liver inflammation can be reversed when the medication is stopped.
 Dr. Abhishek Yadav
Dr. Abhishek YadavChronic hepatitis typically shows no symptoms initially. Fatigue is the most common complaint from those who exhibit symptoms. Fatigue worsens more during the day, and may become debilitating. Other commonly occurring symptoms may include:
People may develop more symptoms if their chronic hepatitis gets worse. These are:
Following are the complications that may be associated with chronic hepatitis:
Chronic hepatitis generally gets identified during a routine blood test because it rarely exhibits any early symptoms. Your doctor may check you for jaundice, tenderness in the abdomen (particularly in the right upper corner above the liver), and visible signs of fluid retention in the abdomen during liver failure if you are suspected to have chronic hepatitis. The blood tests are performed to measure following:
Blood tests for hepatitis B and C as well as for antibodies that indicate autoimmune hepatitis will be performed if these tests reveal evidence of liver inflammation. Your doctor will examine any current or past medication regimens to see if they may be contributing to your chronic hepatitis. Additional blood tests will be ordered to look for unusual causes if the cause is still unknown. To determine the size of the liver, a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound may be performed. The presence of scarred liver tissue is indicative of cirrhosis. A liver biopsy is advised in certain cases. A biopsy involves taking a tiny sample of tissue from your liver, which is then examined under a microscope for detailed investigation for:
With the use of this information, a liver specialist doctor in Pune, India can evaluate your risk of developing liver failure and cirrhosis as well as decide on the best course of treatment. A liver biopsy can also be used to screen for other conditions like fatty liver or alcohol-related liver damage.
Over the past few years, there has been a significant improvement in the prognosis for chronic hepatitis. In fact, many people can now be cured of hepatitis C. The severity of the illness and how well a patient responds to treatment determine the chance of developing cirrhosis. The prognosis is also influenced by age, other medical conditions, the type of virus, and alcohol consumption. Liver cancer risk is increased in individuals with cirrhosis. Early detection is improved with periodic screening that includes a liver ultrasound and blood tests. Talk to your doctor if you suspect symptoms associated with hepatitis immediately.
A: Liver scarring is irreversible. However, the liver can frequently reverse some of the effects of alcohol so that you can lead a normal life. You might receive outpatient care or be admitted to the hospital. Alcohol-related hepatitis cannot be cured with medication.
A: While complete alcohol cessation is often effective in treating mild to moderate forms of acute alcoholic hepatitis. But patients with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis have a poor prognosis.
A: If alcohol consumption persists, alcoholic hepatitis typically develops into cirrhosis. Hepatitis returns to normal in a few months for those who stop drinking, but the cirrhosis that has already set in does not go away.
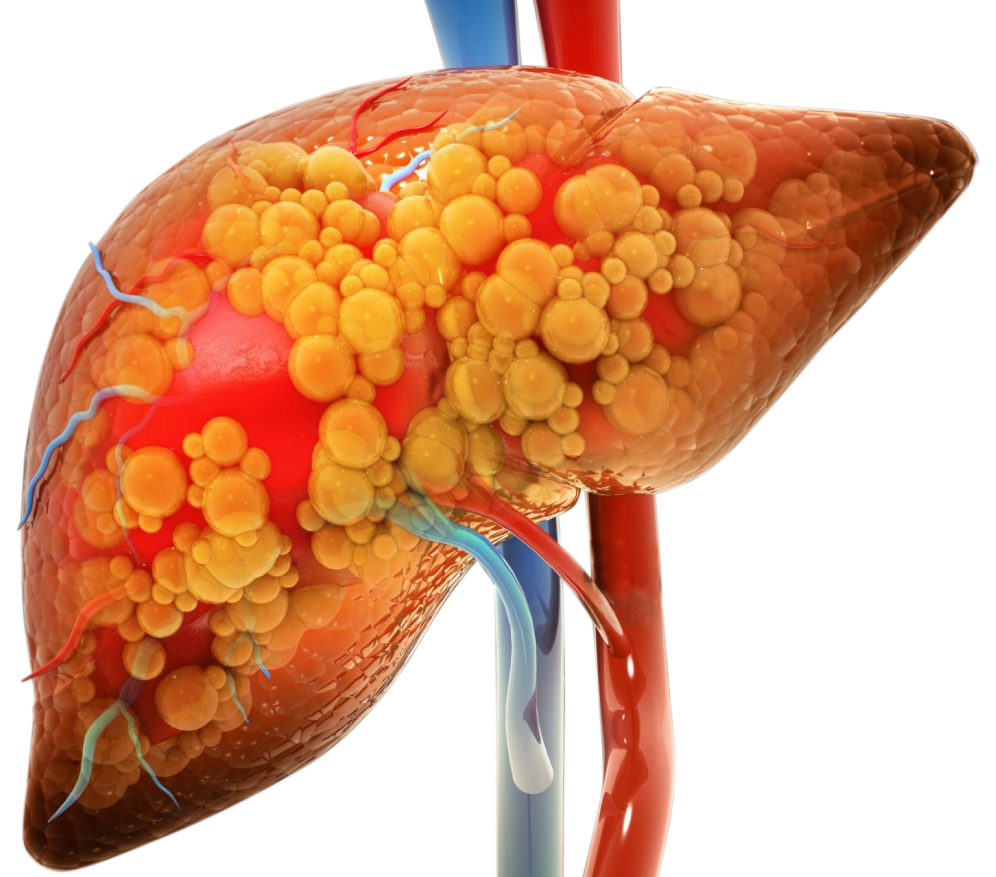
A: The first phase is characterized by the buildup of fat within the liver cells, which is also referred to as fatty liver or steatosis. Alcohol use can occasionally result in alcoholic hepatitis if it continues past this point.
A: Alcohol consumption may result in hepatitis or liver edema and inflammation. This can eventually result in liver cirrhosis, the last stage of alcoholic liver disease. The cirrhosis results in irreversible damage.